Linear Systems - 1 (W9)
- Q1 -

To find the condition number of a matrix A in infinity norm, we can use cond(A, "inf")
clear all
A = [4, 6; 3/5, 1];
cond(A, "inf")Correct answer is 175, in this case, B
- Q2 -

The question asks us to perform the PA=LU factorization of a specific matrix, A=hilb(4). The matrix A is the Hilbert matrix of size 4x4. The PA=LU factorization involves decomposing the matrix A into the product of a permutation matrix P, a lower triangular matrix L, and an upper triangular matrix U. The permutation matrix P represents the row exchanges performed during the factorization process. We need to determine the specific permutation matrix P that corresponds to the factorization of A=hilb(4).
clear all
A = hilb(4);
[L, U, P] = lu(A);
PCorrect answer is;
P =
1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1in this case, C.
- Q3 -

We are given a symmetric matrix A of order 18, where the elements on the main diagonal are 6 and the elements on the lower and upper codiagonals are 3. We are also given a matrix B of size 18x3, where each column is defined by linearly spaced numbers ranging from 0 to j, where j is the column index (1, 2, or 3).
The question asks us to solve the linear systems Ax^(j) = b^(j), where x^(j) represents the j-th column of the solution matrix X and b^(j) represents the j-th column of matrix B. We need to solve these systems for j = 1, 2, and 3.
Finally, we are asked to compute the 2-norm of the vector obtained by summing the solutions of these linear systems.
clear all
A = 6*eye(18) + 3*diag(ones(17,1),1) + 3*diag(ones(17,1),-1);
x=zeros(18,3);
for j=1:3
b=linspace(0,j,18)';
x(:,j)=A\b;
end
s=sum(x,2);
norm(s)Correct answer is 1.8845e+00, in this case, C.
- Q4 -

To find Cholesky factor of a matrix A, we can use chol(A).
clear all
A = [6*pi, 3, 2, 1;
3, 7*pi, 1, 0;
2, 1, 6, 0;
1, 0, 0, 4];
r = chol(A);
r(3,3)Correct answer is 2.4013, in this case, E.
- Q5 -

We are given a square matrix A of size 100. The matrix has the following properties: the elements on the main diagonal are all equal to 4, the elements on the first upper and lower codiagonals are all equal to -1, and the elements on the tenth upper and lower codiagonals are all equal to -2.
The question asks us to compute the condition number of matrix A in the infinite norm. The condition number is calculated in the infinite norm. The final result should be rounded to the first decimal digit.
clear all
A = 4*eye(100) + (-1)*diag(ones(99,1),1) + (-1)*diag(ones(99,1),-1)+(-2)*diag(ones(90,1),10)+(-2)*diag(ones(90,1),-10);
c = cond(A,inf)
round(c,1)Correct answer is 576.5, in this case, A.
- Q6 -

We are given a linear system Ax=b of order 18, where A is a tridiagonal symmetric matrix. The principal diagonal elements of A are all 6, and the elements on the two co-diagonals are all 3. The elements of vector b are linearly spaced numbers in the range [5, 8].
The question asks us to compute the eigenvalues of matrix A. Exploiting the properties of these eigenvalues, we need to find the solution of the linear system Ax=b efficiently by solving two triangular systems. The goal is to compute the 1-norm of the vector obtained by summing the solutions of these two triangular systems.
clear all
A = 6*eye(18) + 3*diag(ones(17,1),1) + 3*diag(ones(17,1),-1);
b=linspace(5,8,18)';
R=chol(A);
y=R'\b;
x=R\y;
s=x+y;
norm(s,1)The code constructs the tridiagonal symmetric matrix A using the eye and diag functions. The main diagonal elements are set to 6, and the elements on the two co-diagonals are set to 3. Then the code performs the Cholesky factorization of matrix A using the chol function, storing the result in matrix R. Then the code solves the lower triangular system R'y = b using the backward substitution operation and stores the result in vector y. Then the code solves the upper triangular system Rx = y using the forward substitution operation / and stores the result in vector x. After the code computes the vector s by summing vectors x and y. Finally, the code computes the 1-norm of vector s using the norm function with order 1.
Correct answer is 4.4944e+01, in this case, C.
- Q7 -

First step of the Gaussian elimination is that, after writing the linear system as an augmented matrix, we need to make the first column zero except the first element by using Elementary Row Operations(ERO). However, we should do it without pivoting.
Correct answer is C.
- Q8 -
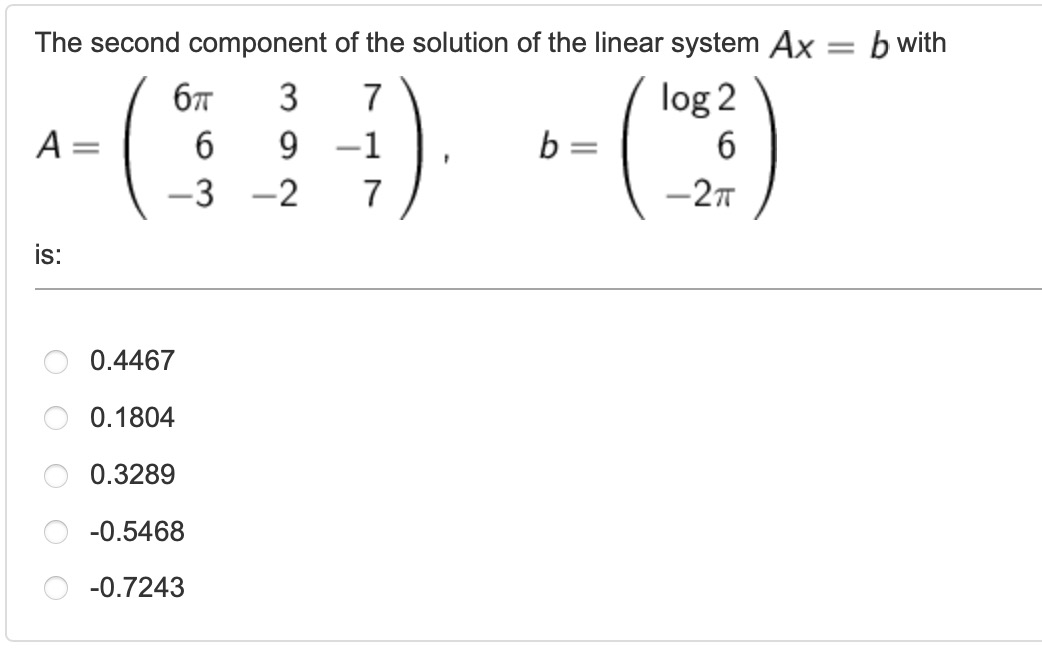
In this question, all we need to do is to solve the linear system. To find the second component of the solution(x), we can use indexing.
A = [6*pi, 3, 7;
6, 9, -1;
-3, -2, 7];
b = [log(2), 6, -2*pi]';
x = inv(A)*b;
x(2)Correct answer is 0.4467, in this case, A.